Want To Understand Why SSDs Are Faster Than HDDs? Read This! 💨
When it comes to computer storage, there are two main options: solid-state drives (SSDs) and hard disk drives (HDDs). SSDs and HDDs differ in technology and performance, but the main difference between the two is their speed. SSDs are generally faster than HDDs, and this is due to the different technologies used in each type of storage device.
In this article, we will explore the reasons why SSDs are faster than HDDs. We will examine the differences in technology between the two types of storage devices and why these differences result in faster performance from SSDs.
⇨ What is a HDD Exactly? 🤔
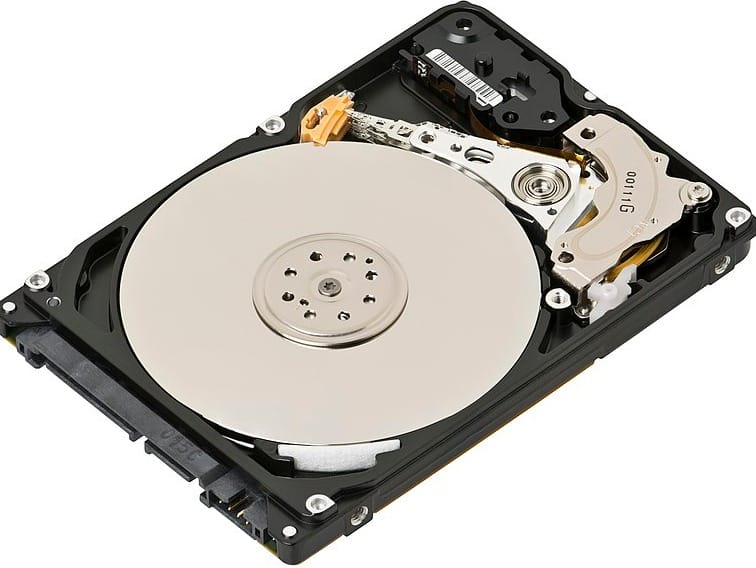

A hard disk drive (HDD) is a device that stores data. It has been around for more than 50 years and has steadily increased its storage capacity while decreasing in size. HDDs use spinning disks, also known as platters, to read and write data.
⇢ How Hard Disk Drives (HDD) Work? ⚙
The internal workings of an HDD consist of one or more magnetically sensitive platters, an actuator arm with a read/write head for each platter, a motor to spin the platters and move the arms, an I/O controller, and firmware that tells the hardware what to do and communicates with the rest of the system.
Each platter is divided into concentric circles called tracks, which are then divided into logical units called sectors. Each track and sector number creates a unique address that helps to organize and locate data.
Data is written to the nearest available area, and an algorithm processes the data before writing to detect and correct errors.
The platters spin at pre-set speeds, ranging from 4200 rpm to 7200 rpm for consumer computers. The higher the pre-set speed, the faster the HDD can read and write data.
⇨ What is an SSD Exactly? 🤔

A solid state drive (SSD) is a type of storage device that uses flash memory. Unlike traditional hard disk drives (HDDs), SSDs do not have any moving parts, making them more durable and reliable. They also run cooler and use less energy.
⇢ How Solid State Drives (SDDs) Work? ⚙
The technology behind SSDs, known as NAND, uses floating gate transistors to store data. These transistors are organized in a grid pattern and further organized into blocks, with each row making up the grid called a page.
An SSD controller keeps track of where data is located and performs other functions.
SSDs can be thought of as large USB drives, as they use the same base technology. They offer superior performance and durability compared to HDDs and are increasingly being used in computers and other devices.
⇨ 5 Main Differences Between SSDs and HDDS
⇛ Difference in Technology 📲
① SSDs (Solid State Drives)
Components (NAND flash memory): SSDs store data using NAND flash memory, which is a type of non-volatile memory that retains data even when power is turned off.
NAND flash memory is made up of cells that can be programmed to store a single bit of data. Each cell has a floating gate that can be charged or discharged to represent a 1 or 0.
Lack of moving parts: Unlike HDDs, SSDs do not have any moving parts. Instead, they use NAND flash memory to store data.
This lack of moving parts makes SSDs more reliable and durable than HDDs, as there is no risk of mechanical failure.
② HDDs (Hard Disk Drives)
Components (platters, heads, spindle): HDDs store data on platters, which are round disks coated with a magnetic material. The data is read and written to the platters by read/write heads that float just above the surface of the platters. The platters are mounted on a spindle and rotate at high speeds to allow for fast data access.
Reliance on mechanical movement: HDDs rely on mechanical movement to read and write data. The spinning platters and moving heads create latency, which is the time it takes for the drive to access the data.
This latency is a major factor in the slower performance of HDDs compared to SSDs.
SSDs are faster than HDDs because they use NAND flash memory to store data, which eliminates the need for moving parts. This lack of mechanical movement results in faster data access and lower latency, making SSDs the faster choice for storage.
HDDs, on the other hand, rely on mechanical movement to read and write data, which creates latency and results in slower performance.
⇛ Access Time 🕞
Access time is the amount of time it takes for a storage device to read or write data from its storage media. It is measured in milliseconds (ms) and is an important factor in determining the overall performance of a storage device.
Access time is particularly important in situations where data needs to be accessed quickly, such as in gaming or video editing.
① SSDs - Instantaneous access
SSDs have no moving parts, which means they can access data almost instantaneously. The NAND flash memory used in SSDs allows for fast read and write speeds, resulting in low access times.
This means that the storage device can start working on a task almost immediately after it is requested, which improves the overall speed of the system.
For example, when a user clicks on a program to open, an SSD can access the data and start the program almost immediately.
This results in a faster and more responsive system, which is particularly important for users who work with large amounts of data or run multiple programs at once.
② HDDs - Delayed access due to mechanical processes
HDDs rely on mechanical processes to read and write data, which creates latency. The read/write heads on an HDD need to physically move to the location of the data on the disk, which takes time. This delay in access time can slow down the overall performance of the system, especially when dealing with large amounts of data.
For example, when a user tries to open a program, an HDD may take longer to access the data and start the program. This results in a slower and less responsive system, which can be frustrating for users who work with large amounts of data or run multiple programs at once.
⇛ Data Transfer Rates ⚡
SSDs have significantly faster data transfer rates than HDDs. This is due to the difference in technology used in each type of storage device.
SSDs use NAND flash memory to store data, which allows for faster read and write speeds than the mechanical processes used in HDDs.
① Read/write speed of SSDs
SSDs have read and write speeds of up to 5,500 MB/s and 500 MB/s, respectively. This means that SSDs can transfer data at a much faster rate than HDDs.
The faster read and write speeds of SSDs mean that data can be accessed and processed faster, resulting in a more responsive and efficient system.
For example, when transferring a large file from one location to another, an SSD can do so much faster than an HDD.
This can save time and improve productivity, particularly for users who work with large amounts of data.
② Read/write speed of HDDs
HDDs have read and write speeds of up to 200 MB/s and 150 MB/s, respectively. This is significantly slower than the speeds of SSDs, which can result in slower system performance. The slower read and write speeds of HDDs mean that data can take longer to access and process, resulting in a less responsive and less efficient system.
For example, when transferring a large file from one location to another, an HDD may take longer to complete the transfer than an SSD. This can result in slower system performance and reduced productivity, particularly for users who work with large amounts of data.
⇛ Fragmentation 🤏
Fragmentation is the process of breaking a file into smaller pieces and storing them in different locations on a storage device.
This can occur when a file is deleted and new data is written to the storage device in the same location. The result is a file that is spread out across the storage device, which can slow down data access times.
SSDs do not have the same physical limitations as HDDs, which means that fragmentation has less of an impact on their performance. SSDs can handle fragmentation more efficiently than HDDs, which means that the impact on speed is minimal.
For example, even if a file on an SSD is fragmented, the storage device can still access the data quickly due to its fast read and write speeds.
⇛ Durability and Reliability 💪
① SSDs - More reliable due to lack of moving parts
SSDs do not have any moving parts, which makes them more reliable than HDDs. The lack of moving parts means that there is less chance of mechanical failure, which can result in data loss.
SSDs are also less susceptible to damage from physical shock or vibration, which makes them a good choice for laptops or other portable devices.
② HDDs - Susceptible to mechanical failures
HDDs rely on mechanical processes to read and write data, which makes them more susceptible to mechanical failure.
The spinning platters and moving heads on an HDD can wear out over time, which can result in data loss.
HDDs are also more susceptible to damage from physical shock or vibration, which can cause the read/write heads to crash into the platters and cause data loss.
⇨ What are HDDs Best For❓
If you need to store large amounts of data that you don't need to access frequently, an HDD is a great option.
It's also suitable for those with modest computing needs and for those who are buying or building a PC on a budget. HDDs are still reliable for external backup options.
What does an HDD mean for employees in 2023? Employees who primarily use Microsoft Office and similar programs won't be too affected by using an HDD.
However, those who work with very large files and on intensive tasks and programs will struggle with an HDD.
The bottom line is that if you have the budget for it, an SSD is the better option. However, if you're on a tight budget and don't need the specific benefits of an SSD, an HDD is still a reliable option.
It's a good idea to use an HDD cleaner to free up space and keep your clutter as low as possible.
⇨ Who are SSDs Best For❓
Those who use resource-intensive programs like multimedia editing suites, gamers who want to play new games, and anyone who opens and copies files from their drive often will benefit the most from an SSD.
An SSD is ideal for those who move data frequently, such as huge, uncompressed video files or 3D-modeling modules used in engineering and medicine.
Additionally, SSDs are great for copying and pasting lots of data from one drive to another, as well as loading rich video game environments.
Overall, if you can afford it, an SSD is a better option than an HDD, especially if you need fast data transfer speeds and frequent access to large files.
Conclusion - SSDs Are Faster But HDDs Are Still Useful!
SSDs are faster than HDDs due to the technological differences between the two types of storage devices. SSDs use NAND flash memory to store data, which allows for fast read and write speeds, low access times, and minimal fragmentation.
HDDs, on the other hand, rely on mechanical processes to read and write data, which creates latency, higher power consumption, and susceptibility to mechanical failure.
While HDDs may still be a better choice for certain applications due to their lower cost and higher storage capacity, SSDs offer faster performance and greater reliability.
When choosing a storage device, it is important to consider the specific needs of the user and the application in order to make the best decision.
More For You ⬇💻⬇